| | 600 |
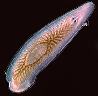 |
| Around
600 mya the earliest animals, Sponges appeared. Then Ctenophora
(right) evolve neurons, mouths and a digestive system. Flatworms
(left) are the first to develop a basic brain. |
|  |
|
| | | Timeline:
The Last 500,000,000 Years |
| | 550 |
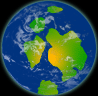 |
| 550
mya: Earth's protective Ozone layer forms and land as the potential
for life. The second supercontinent, Pannotia, forms, then quickly
breaks up by 540 million years ago. | |  |
|
| | 540 |
 |
| The
Cambrian 'explosion' is a incredibly quick divergence of life. Trilobites
and the 2 metre long, Anomalocarid (right) thrive. Fish-like
Pikaia develop the earliest backbone-like feature. |
|  |
|
| | 530 | |
| | 520 | |
| | 510 |
 |
| 505
mya. Earliest vertibrates include jawless Agnatha fish such as Myllokunmingia
(right) which have internal skeletons. | | 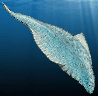 |
|
| | 500 | |
| | 490 |
1st
MASS
EXTINCTION
488 mya | Cambrian-Ordovician
transition. This event eliminated many brachiopods and conodonts and severely
reduced the number of trilobite species. |
 | Placodermi:
The first fish evolve jaws. | |
| | 480 |
 |
| 475
mya. Green algae on the edge of lakes evolves onto land to become the first
plants in the form of Lichen and moss, along with fungi. |
|  |
|
| | 470 | |
| | 460 | |
| | 450 |
 |
| Arthopods
develop endoskeletons and millipedes are some of the first land animals,
then spiders and scorpions. | |  |
|
2nd
MASS
EXTINCTION
| 444
mya: The Ordovician-Silurian extinction changes marine life drastically. |
| |
| | 440 | |
| | 430 |
 |
| 428
mya. The earliest known complex plant is Cooksonia,
a very simple branching plant with no seeds or flowers. This would have been the
most complex flora on the Earth for many millions of years. | |
|
| | 420 | |
| | 410 | |
| | 400 |
 |
| 400
mya on land the first insects appear, including silverfish (left).
In the oceans, Coelacanth (right) evolves, both of which survive
today. | |  |
|
| | 390 | |
| | 380 |
 |
| 375
mya. The fish Tiktaalik evolves adaptations to shallow-water
habitats with arm-like structures and a flexible head. On land, Archaeosperma
evolves the first seeds. | |  |
|
| | 370 |
| Cladoselache:
The first known shark |  |
|
364
mya
3rd MASS
EXTINCTION | The
Late Devonian extinction mass massive and wiped our about 70% of all species over
a period of about 20 million years. | | |
| | 360 |
 |
| 360-280
mya was the "golden age" of sharks of which Stethacanthus
was an example (left) but the 10m long armoured fish Dunkleosteus
(right) was the top predator. | |  |
|
| | 350 | |
| | 340 |
|
| | 330 | |
| | 320 |
|
| | 310 | |
| | 300 |
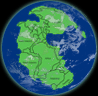 |
| Supercontinent
Pangea forms, the most recent time all the continents were one.
The first reptile Hylonomus, (right) evolves
through the development of amniotic egg. | |  |
|
| | 290 |
 |
| Insects
evolve flight, including dragonflies which still
survive today. Cycads appear. Horsetails and
tree ferns (left) are everywhere, one day to become modern fossil
fuels. | |  |
|
| | 280 |
 |
| Giant
dragonflies with 2ft wingspan evolve. Vertibrates have developed into amphibians
like Temnospondyli and reptiles such as Edaphosaurus (right)
appear with its distinctive sail. | |  |
|
| | 270 | |
| | 260 |
 |
| 256
mya Diictodon (left) and Dinogorgon (right)
are two mammal-like reptiles which thrive. | |  |
|
| | 250 |
| 4th
MASS EXTINCTION 251 mya - The Worst in Earth's History |
The
Permian-Triassic extinction devastated Earth, wiping out 96% of species in the
ocean and 70% of life on land. It has been suggested that the Wilkes Land crater
in Antarctica is the legacy of a 30-mile-wide meteorite which caused it and broke
up Gondwana. | |
| | 240 |
 |
| Herbivore
Lystrosaurus (left) is one of the few that survives the extinction.
Archosaurs (right) diverge from other reptiles. Oxygen levels
are down from 30% to 10%. | |  |
|
| | 230 | |
| | 220 |
 |
| The
earliest mammal ancestors such as Cynodonts (left) suckle their
young and are truly warm-blooded. The first dinosaur, Coelophysis
(right) is capable of walking upright. | | 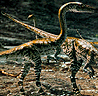 |
|
| | 210 |
 |
| The
largest-ever land animals are now dinosaurs, such as 10m long herbivore Plateosaurus
(left) but archosaurs like Postosuchus (right) are the dominant
preditors. | |  |
|
| | 200 |
| 5th
MASS EXTINCTION 200 mya - End of the Archosaurs |
The
Triassic-Jurassic extinction saw 20% of all marine life die along with the dominant
land animals: The archosaurs. Most therapsids and the remaining large amphibians
vanished but dinosaurs thrived. | |
| | 190 |
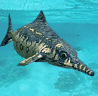 |
Reptiles
such as Ichthyosaurs (left) and Plesiosaurs
(right) dominate the waters. Modern amphibians such as frogs
and salamanders appear. | |  |
|
| | 180 |
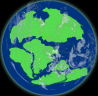 |
| Pangea
splits up into Gondwana in the south and at this stage modern-day
Antarctica is dominated by forests. Eurasia is joined to North America making
up Laurasia in the north and new species develop due to the water
barriers created by the separation. | | |
| | 170 |
164
mya. Castorocauda lutrasimilis is the oldest swimming mammal and the ancestor
of similar present-day water-loving creatures such as the platypus. |
|  |
|
| | 160 |
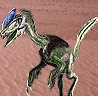 |
| Guanlong
wucaii is the earlest Tyrannosaur. It was 3m long and
lived in the area which is now north west China. It displayed a long, delicate
nasal crest for display and was probably had a fibrous covering which was the
precursor to feathers. | | |
| | 150 |
 |
| In
the golden age of dinosaurs giant dinosaurs are common, including the Stegosaurus
(left) reaching 10-12m, and the predator Allosaurus (right). |
|  |
|
| | 140 |
 |
| Brachiosaurus
(right) reached 14m high and 40 tonnes, while in the air, the earliest known bird
Archaeopteryx (left) takes to the skies, carrying many dinosaur features. |
|  |
|
| | 130 |
 |
| 135
mya Iguanadon appear. Microraptor has bird-like feathers.
125 mya Doormouse-like Eomaia (left) is the ancestor of modern
placental mammals. Plants evolve flowers. |
|  |
|
| | 120 |
 |
| Bird
evolution diversifies with varieties such as Confuciusornis
(left). Dinosaurs on the ground had feathers in various degrees of sophistication,
such as Sinornithosaurus (right). | |  |
|
| | 110 |
 |
| Largest
crocodile Sarcosuchus (12m) lived (left). Deinonychus and Spinosaurus
(right) appeared. Tallest dinosaur, Sauroposeidon lived. Earliest modern bird
appeared, Gansus. | |  |
|
| | 100 |
 |
| In
south America, giants ruled. Giganotosaurus (left) was the biggest
land carnivore (13.7m long) probably hunting the massive long-neck Argentinosaurus
(35m) (right). | |  |
|
| | 90 |
 |
| Flowers
allow plants to thrive and so herbivore dinosaurs such as duck-bills (left) are
massively successful and medium-sized meat-eaters have plenty of prey, e.g. Alectrosaurus
(right). | |  |
|
| | 80 |
 |
| Some
of the most famous dinosaurs lived: Horned Parasaurolophus (left),
many-pronged Styracosaurus, bird-like Oviraptor
and vicious, feathered Velociraptor (right). |
|  |
|
| | 70 |
 | Tyrannosaurus
rex appeared just
67 mya, and preyed on Triceratops. |
| 6th
MASS EXTINCTION 65 mya - End of the Dinosaurs |
Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction saw 50% of all species gone, probably by meteor. |
|
| | 60 |
 |
| With
no dinosaurs, mammals thrive, such as Plesiadapis (left), a very
early squirrel-like primate. Top predators were Creodonts (right). |
|  |
|
| | 50 |
 |
| Hyracotherium
(left) is the earliest horse. The ancestors of whales and dolphins is Ambulocetus
(right) which could walk on land and swim. The first elephant is 1m high Moeritherium. |
|  |
|
| | 40 |
 |
| 2m
bird Gastornis (left) was a top predator. Primates diverge at
40 mya. Whales' ancestors can no longer move on land. 35 mya grasses
evolve. Cynodictis will become modern dogs. |
|  |
|
| | 30 |
 |
|
Proailurus will give rise to all cats. Possible human ancestor
Aegyptopithecus (right) splits from monkeys. Rhino relative Indricothere
is 4.5m tall. The Himalayas form. | |  |
|
| | 20 |
 |
|
Giant sloth Megatherium is 6m (left). The largest-ever bird Argentavis
(right) has a 7m wingspan. Megalodon is a 15m long shark. Our
ancestors diverge from gibbons' ancestors. | |  |
|
| | 10
0 |
 |
|
7mya - 3m tall Gigantopithecus (left) was the largest ape ever.
3 mya australopithecines walked upright. Sabre-tooth
cats appear. 100,000 ya, anatomically modern humans. |
|  |
|